What is BIM?
..And what are the advantages?
Collaboration and good visualisation of information are becoming increasingly important in the construction industry. Deadlines are becoming tighter, the quality must be better and better, and budgets are often limited. The classic construction drawing is often no longer sufficient for building projects in the digital age. Instead, more and more construction companies and contractors are working with BIM models. But what exactly is BIM? And what are the advantages? You can read it in this article.
An important difference with an ordinary building drawing, is that BIM not only has a geometric dimension. It also displays information about the properties of the various elements and components of the structure.
What is BIM?
BIM originally is the abbreviation for Building Information Modelling, but the term building information model is also being used sometimes. Both names mean the same thing and already give away a little of what BIM is: a digital model that forms a virtual representation of a building. The model consists of objects, to which information is linked.
An important difference with an ordinary building drawing, is that BIM not only has a geometric dimension. It also displays information about the properties of the various elements and components of the structure. Think of colours, materials, technical properties and the relationship to other objects.
Take a wall, for example. In BIM, you can record not only where it should be built, but also the material it will be made of (reinforced concrete, masonry), what it will cost to build the wall and the colour of paint you will use to paint it. All object-oriented information can easily be linked to things such as foundations, construction phases, functions, the required structural strength or the connection to surrounding objects. The various parties involved in the building process, from contractor to architect and from window-frame maker to mason, can add information to a BIM model.
BIM-viewers
The models can be viewed in a BIM viewer. This is a special tool that, with a few mouse clicks, shows all the information about the construction. Moreover, the client can use the tool to see whether the work has been delivered as agreed. With a BIM viewer, you can quickly see whether all the data required for the proper execution (information delivery specification) of the project have already been processed in the models that your construction professionals work with. That way, you always know what stage a project is in. With a BIM viewer, you can also easily share and discuss models and current projects with project team members, colleagues and authorised external partners (e.g. subcontractors and suppliers).
Many viewers have various display options. For example, you can choose to show the model of the architect or structural engineer separately, but also show all models integrally.
There are various BIM viewers on the market. Dalux is a much-used viewer, mainly because of its user-friendliness and relatively low entry threshold. But the Rolls-Royce among BIM viewers is the Autodesk Forge 3D Viewer. This BIM viewer offers freedom of model format (you can choose IFC or RVT) and provides advanced development tools that allow you to check the properties of all objects in a model against the calculations made.
In addition, it is possible to view and analyse the individual elements of a building in detail by virtually splitting the drawn structure into different components. You can also use the tool to show horizontal and vertical cross-sections of a structure and take a virtual walk through the building.
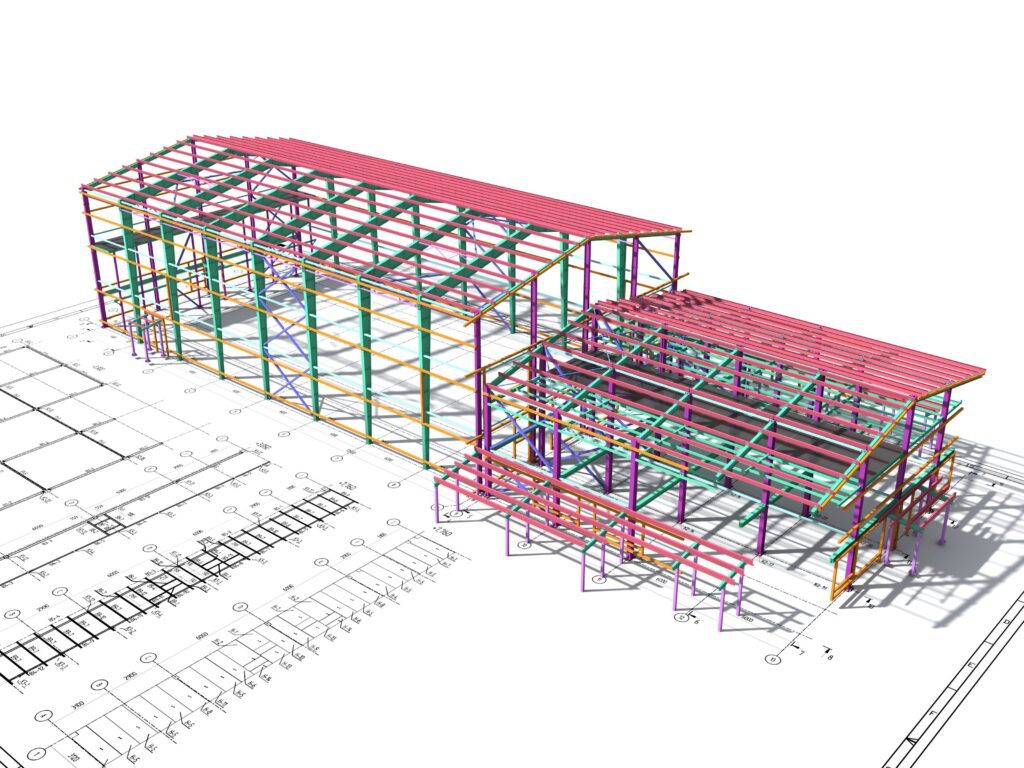
The advantages of BIM
Working with BIM has many advantages for building contractors and all other stakeholders involved in a construction project. We explain the most important ones.
Drawings are always up to date
BIM allows you to immediately implement approved changes in drawings and objects in the rest of the model. You therefore do not have to continually check manually whether drawings are still up-to-date. That saves a lot of time, phone calls and e-mails.
Reduced failure costs
Due to the density of information and the possibility of updating that information quickly and easily, BIM reduces failure costs. You notice any design errors earlier and do not have to make major structural alterations afterwards. That saves money, but it also reflects positively on the reputation of a construction company, contractor or project developer.
Better cooperation
BIM stimulates and streamlines cooperation between the various parties (architects, project developers, contractors, subcontractors, suppliers) involved in a construction project. Instead of them all operating from their own little islands, all parties involved can share information and share the results of their plans and work. Exchanging data is faster and easier. There is no need for a major translation. The result? More mutual understanding and a greater chance of an end result that satisfies everyone.
Enthusing effect
With BIM models, you present visualisations of a construction project at an early stage. This often has an enthusing effect on stakeholders and clients. They see in concrete terms what is planned and can quickly give feedback on designs. A BIM model is therefore a powerful tool for an architect or project developer to convince a client of his vision.
All information in one central place
Because everyone works in the same BIM model, all relevant information about a building project (materials, dimensions, colours, suppliers) can be found in one central location. You build up a digital library of information, as it were. Chain communication improves and unnecessary research is a thing of the past. Because BIM ensures that you work with the same standards (IFC) in every phase of the construction process, it is also easier for builders to ensure a consistent level of quality.
Easier maintenance
A BIM model continues to provide added value, even after the construction work has been completed. Has something broken down, for example? With BIM, you immediately have the information you need to carry out a repair or replacement. You no longer need to take extra measurements or dig through a thick paper file to find the right information. Instead, you find everything you need to know in the BIM model.
BIM is now part of the game
BIM has taken off both nationally and internationally. The majority of construction companies are already working with the technology. Logical, given the various advantages the method brings. Nevertheless, there are still builders who make little or no use of BIM. For those companies, there is still a world to be won.
Would you like to introduce BIM in your organisation? Then first try to immerse yourself in the subject, for example by reading relevant articles, blogs and white papers on the subject and by watching webinars. It also helps to approach a partner who specialises in BIM issues. Once your knowledge base is solid enough, are you really going to ‘BIM’? Then make sure you get the entire organisation on board and roll out the method step by step. Good adoption is also the key to success with BIM.
Read the next article: “What is intranet?“